ABSTRACT
The Fen River, located at the Loess Plateau in Shanxi Province, is one of the most important life sources for local people. Most residents in the past relied on farming to make life. As the only riverway that could serve for irrigation in the region, Fen River provided a huge amount of water. In addition, nearby lands were vastly used for agricultural purposes. The river acts as a spine to support people’s life for a long time. It is also called as the Mother River in the region.
However, as cities in the region quickly developed over past decades, past farmlands have gradually replaced by concrete and skyscrapers. Existing farmlands are squeezed to the city' s edges. Furthermore, rural life and agricultural practices gradually retreat from people' s current life. People who memorize the past rural life can only find them outside of city and in mountain areas. Current water use also switches to industrial development, some agriculture, etc.
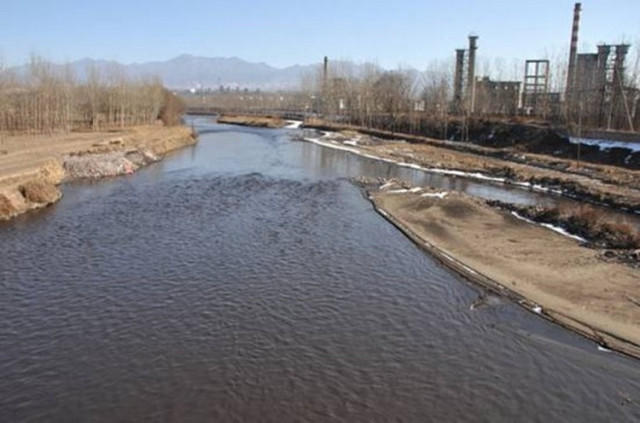
From environmental perspective, the river starts to meet a lot of issues because of human activities, including water pollution, wastewater discharge, etc. The river also become discrete from people’s life and production. Now, we won’t say Fen River is the mother river that offers us huge benefit, but we ignore it and discard it accompanied with past rural practices.
I don’t want to let the mother river down and disappeared in our life. This river as a carrier has already linked multi-decade culture and history in the region. I believe it could adapt to current changes and civilization and reconnect water, rural and urban landscape, as well as human life.
Fen River
Image

WATERSHED ANALYSIS
This chapter is mainly focusing on the river body of Fen River, both from its regional watershed scale and from the small park itself.
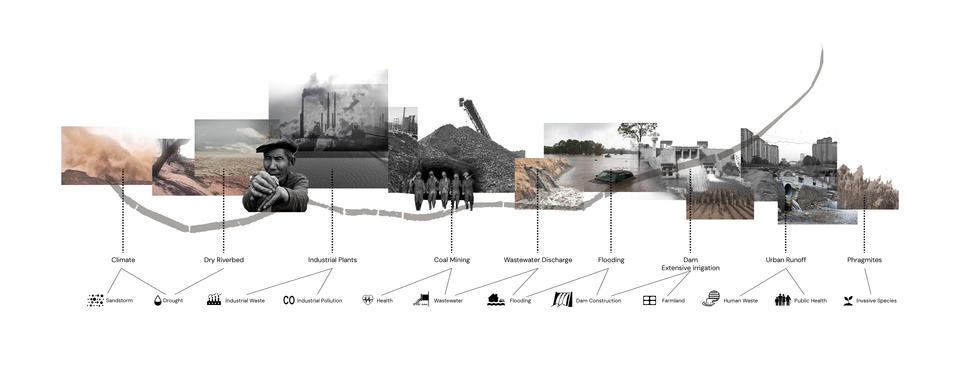
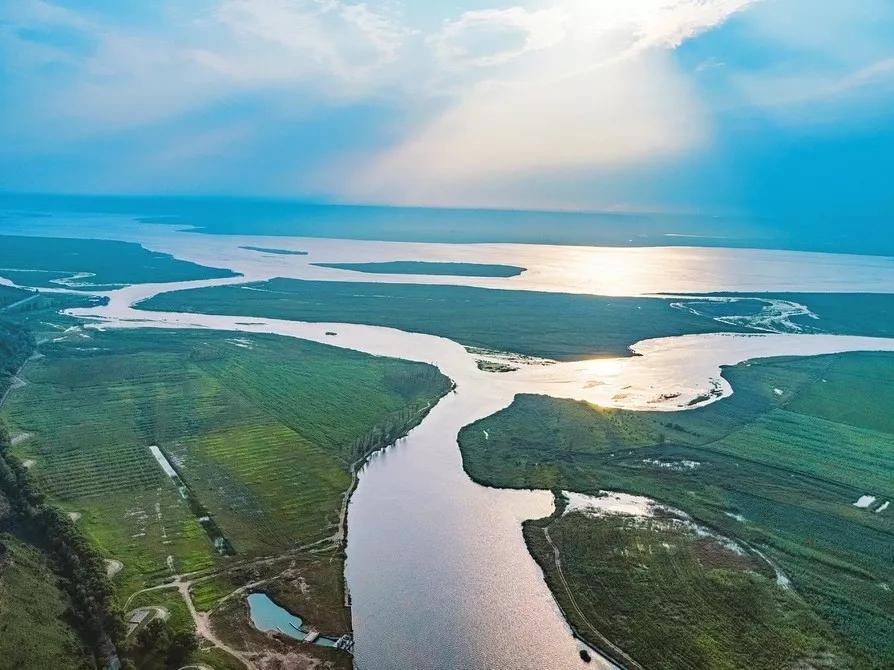
Fen River is the second largest tributary of Yellow River. It feeds the whole region’s agriculture, human lives, and industries. It is also named as the Mother River in the province. However, it also struggles for much outside pressure caused by human and nature. This chapter is going to introduce the watershed system, land reclamation, and issues Fen River is facing.
Image
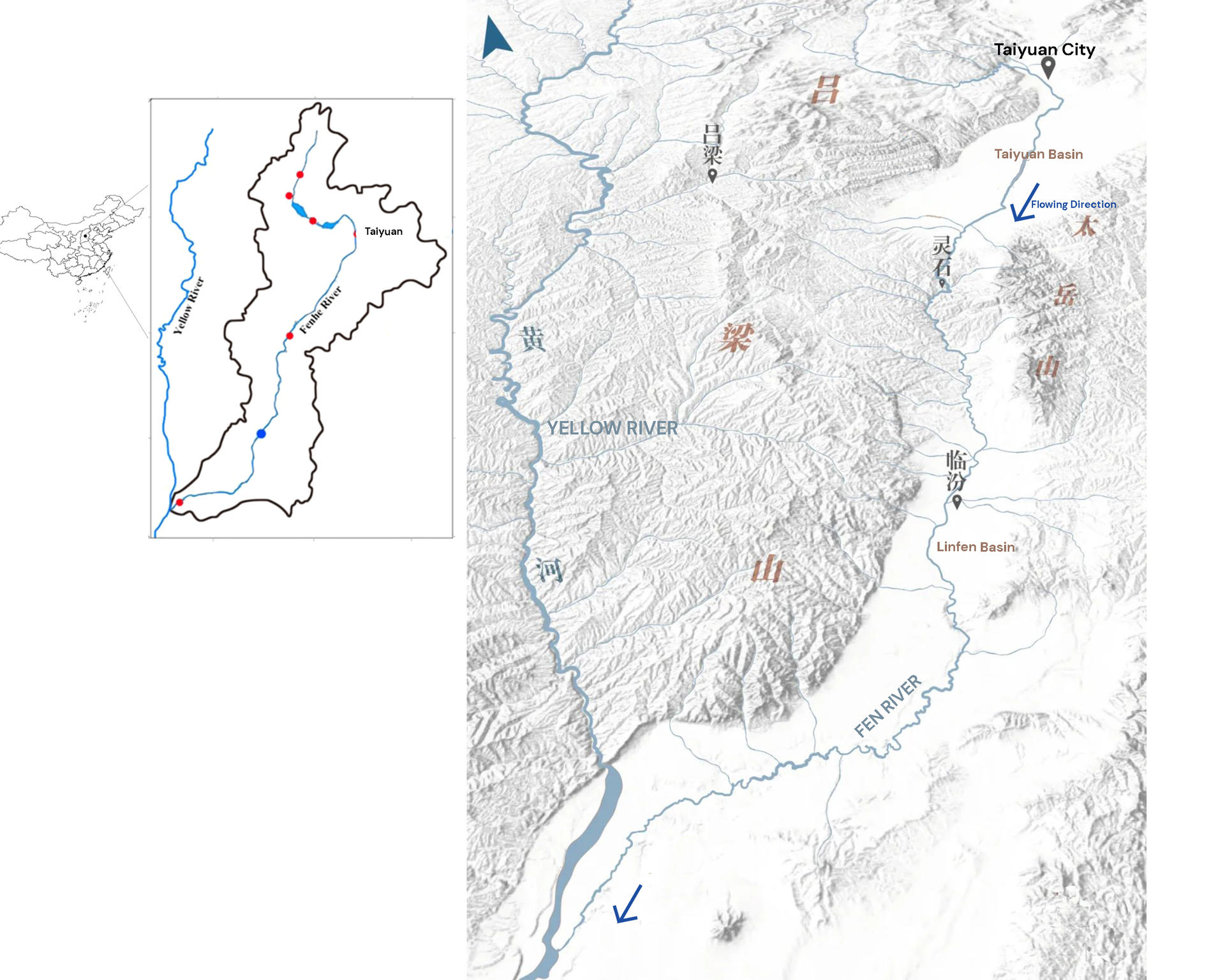
▲ Image 1: Fen River is located on loess plateau in Shanxi Province. It is a tributary River of Yellow River. Fen River is an important bond that link numerous rural and urban scapes, people and cities, as well as history and present.
Current Usage of Fen River gradually shifts from agriculture to industry and city services. Right now, it still provides huge waterpower for industrial development and coal mining in the mountain and downstream, water resource for farmland irrigation, waterfront park for recreation in cities, etc. It acts as a spine to support regional economic and environmental development.
Image
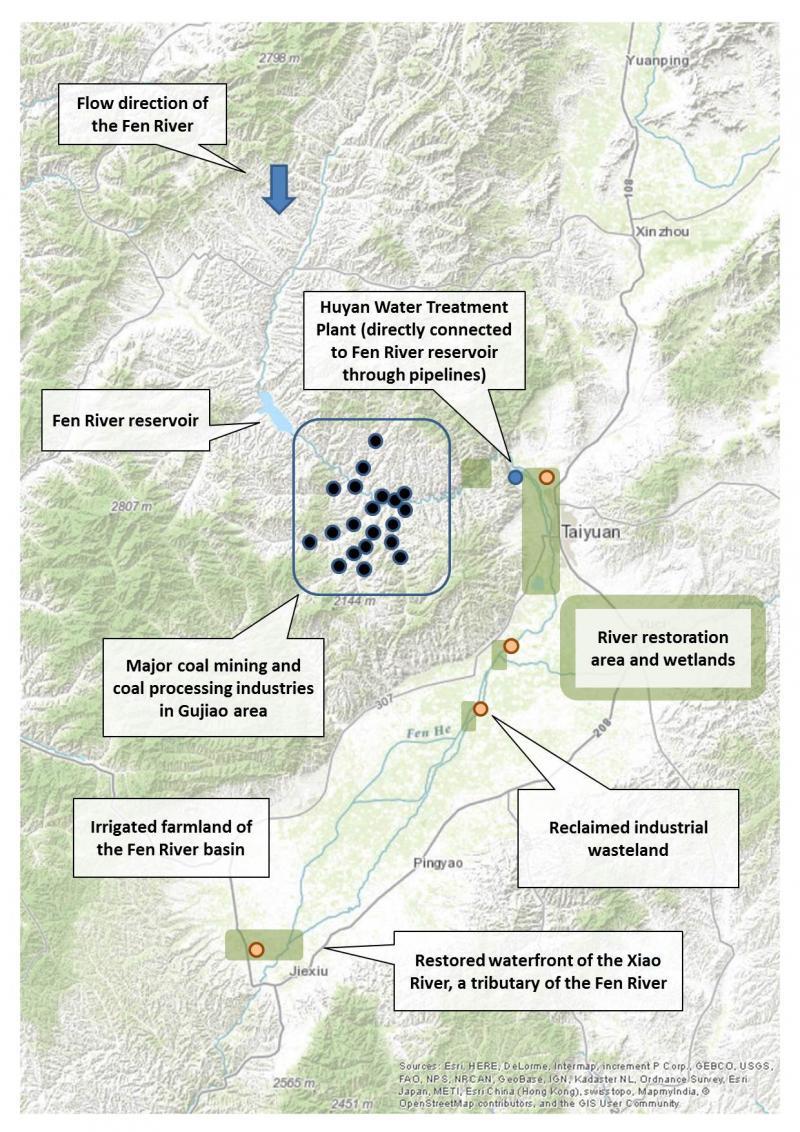
▲ Image 2: Land Reclamation Map of the Region
Issues Fen River Is Facing
TAIYUAN CITY
Image
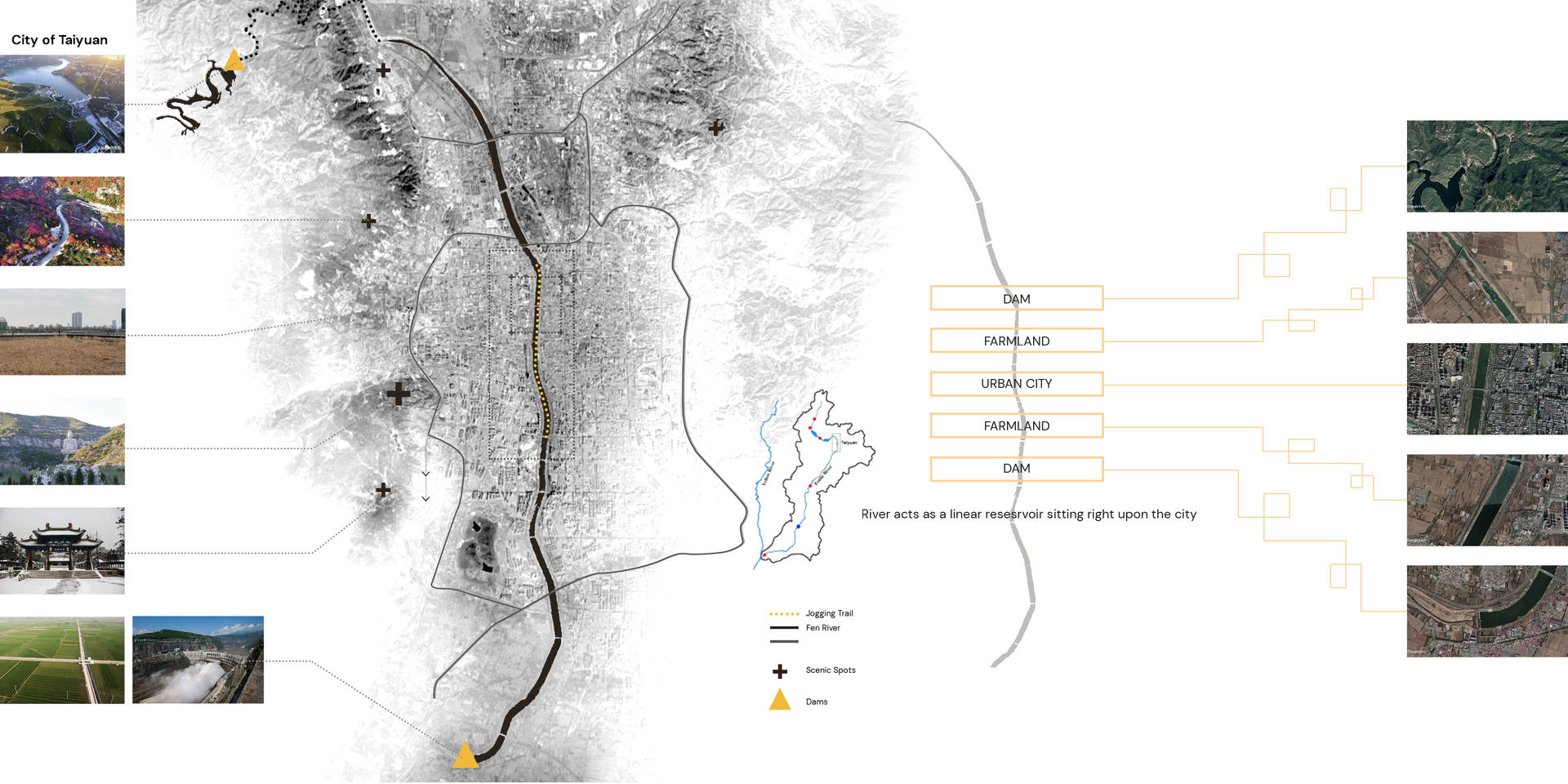
▲ The main testing ground is the Taiyuan City where has both urban city and rural farmlands. The Fen River in the city is very fragmented. It is like a linear reservoir sitting still in the middle of the city. This segment of river is framed by two dams and two pieces of farmland. Right now, this river only serves for city beautification, and has very few practical functions. The body of river seems really discrete from the large watershed.
Image

▲ The image above shows the transition from rural to urban life.
Image

▲ The image shows the Fen River Waterfront Park in Taiyuan, which only serves for city beautification purpose and with few practical programs.
THESIS PROPOSAL
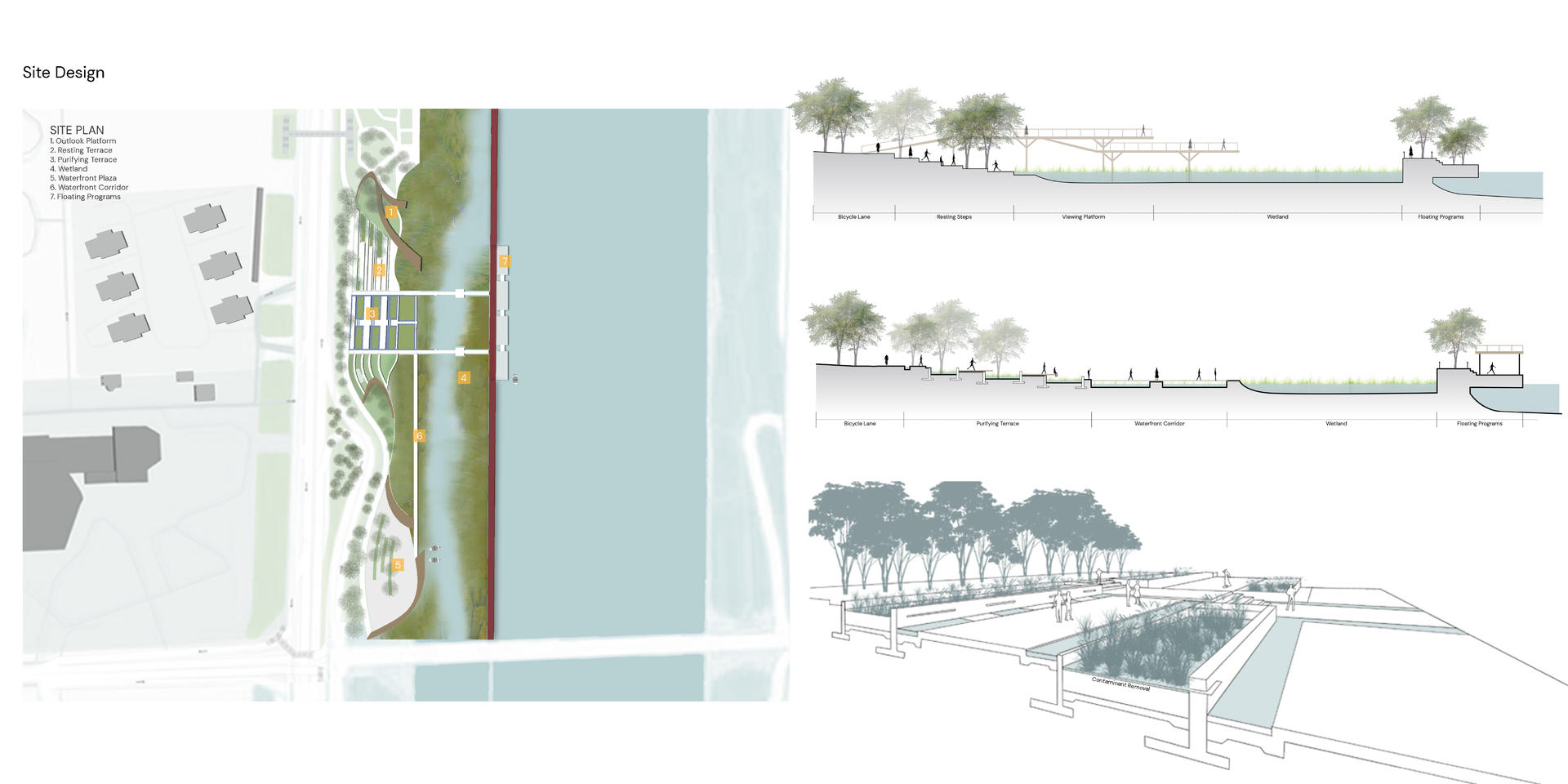
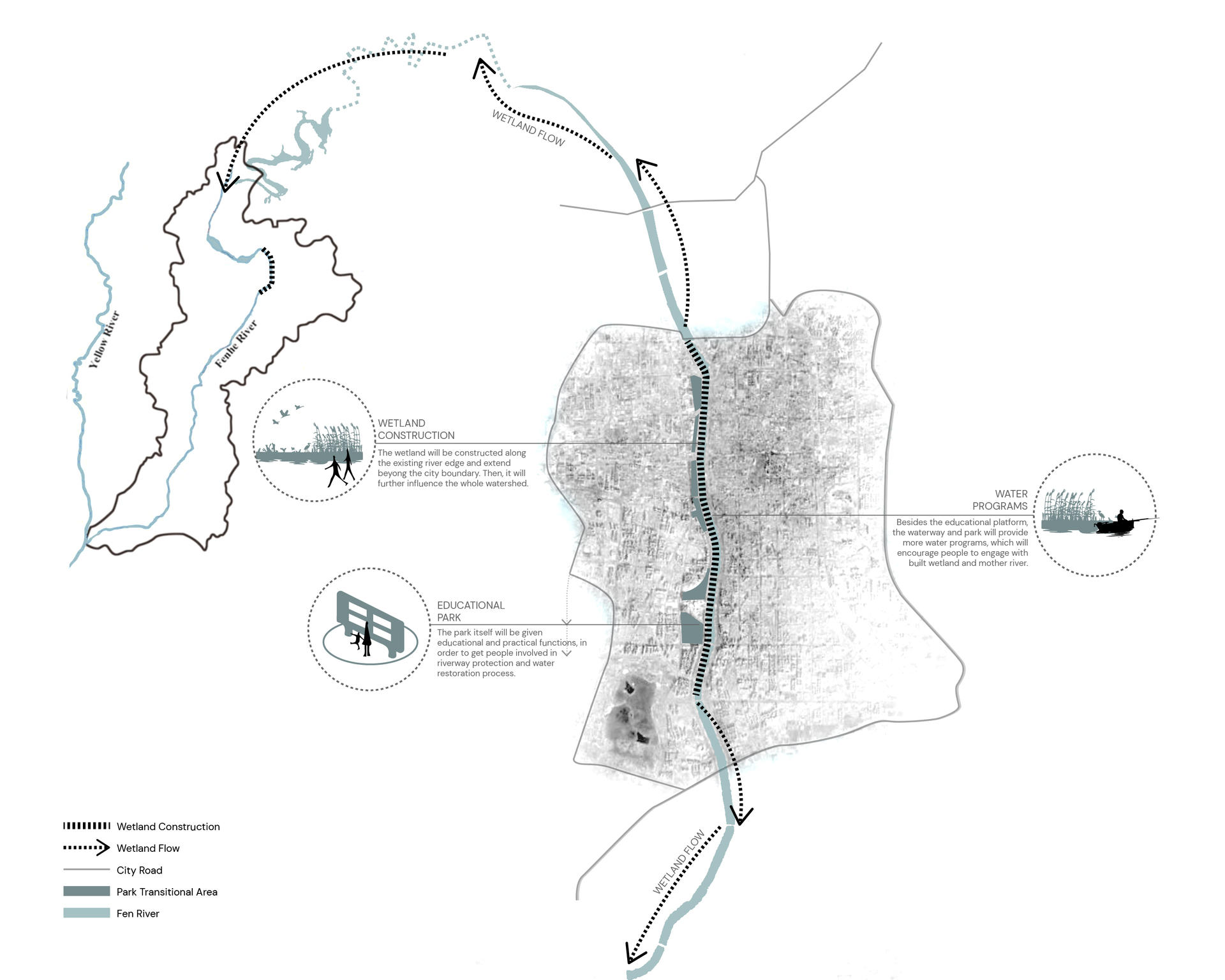
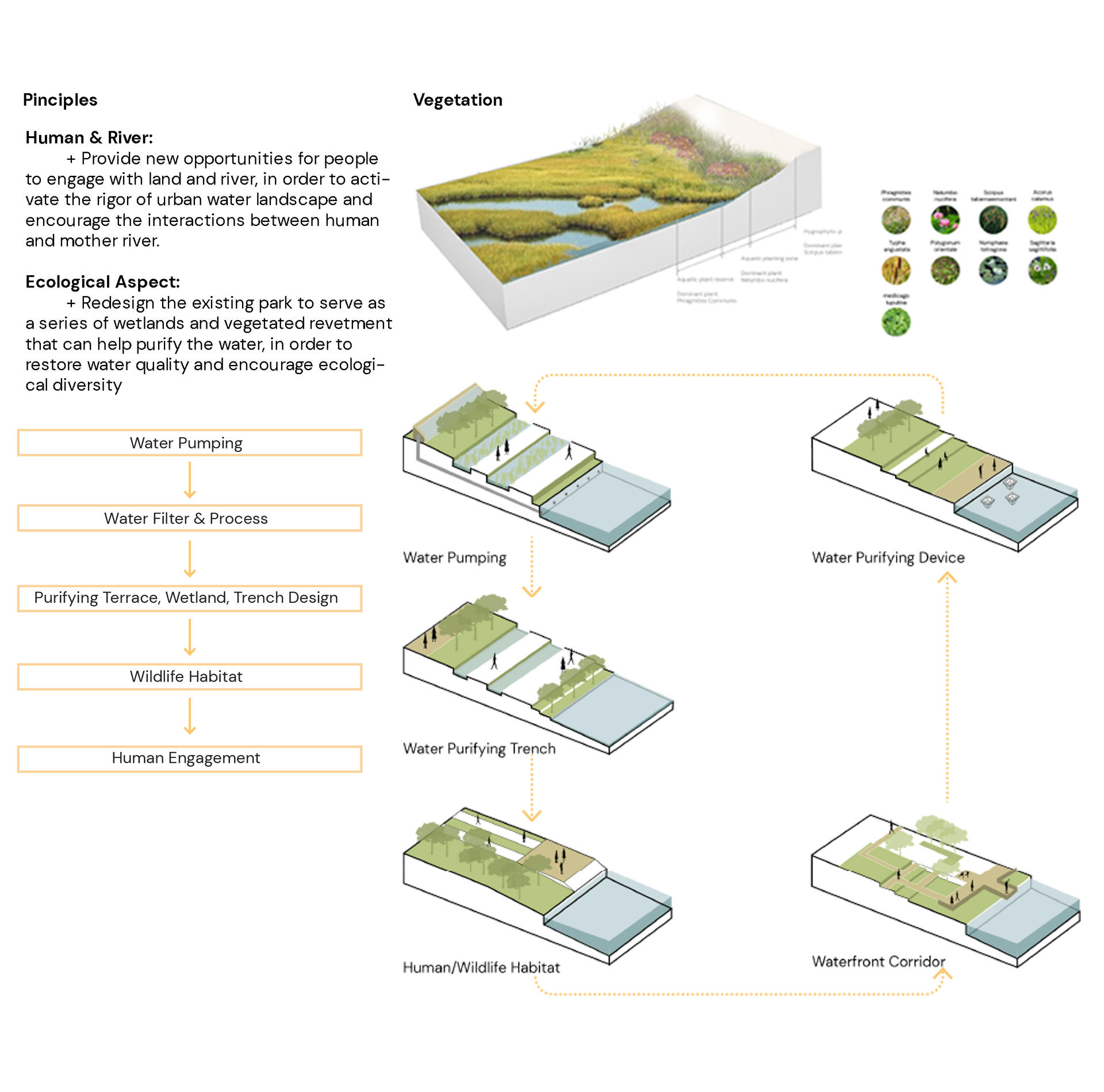
The project aims to build on the Fen River and existing waterfront park in Taiyuan City as a nursery to restore water quality and as a linkage to reach out surrounding rural and regional landscape. The whole project is involved with water remediation, wetland restoration, and agricultural practices in the long run. The key design goals are to remediate water via wetland construction, create educational platforms to transit waterway protection, and interact with agricultural production in the future. The project will transform the existing waterfront park into a water nursery for ecological conservation, which will then spread out to the whole watershed, as well as agricultural tourism, which will bring outside rural landscape back to the city. It will then contribute to new sets of opportunities for people to engage with land and river, as well as communicate to a bigger landscape.
The first phase is restoration, which aims to clean up Fen River by wetland construction. The wetland plants will grow along the river edge and gradually extend beyond the city boundary. City will become a steward to take care of the river. Then, it will feed and influence the whole river system. And in this phase, the park will be given educational functions, in order to get people involved in wetland study and riverway protection process.
Here comes the living water system, which will pump water to the park, and then flowing through the purifying terrace and wetland plants. As plants absorb and break down the pollutants, the water will be filtered and cleaned up. This will be a long-term process to purify the whole waterway.
Image
▲ Phase 1: Restoring
Image
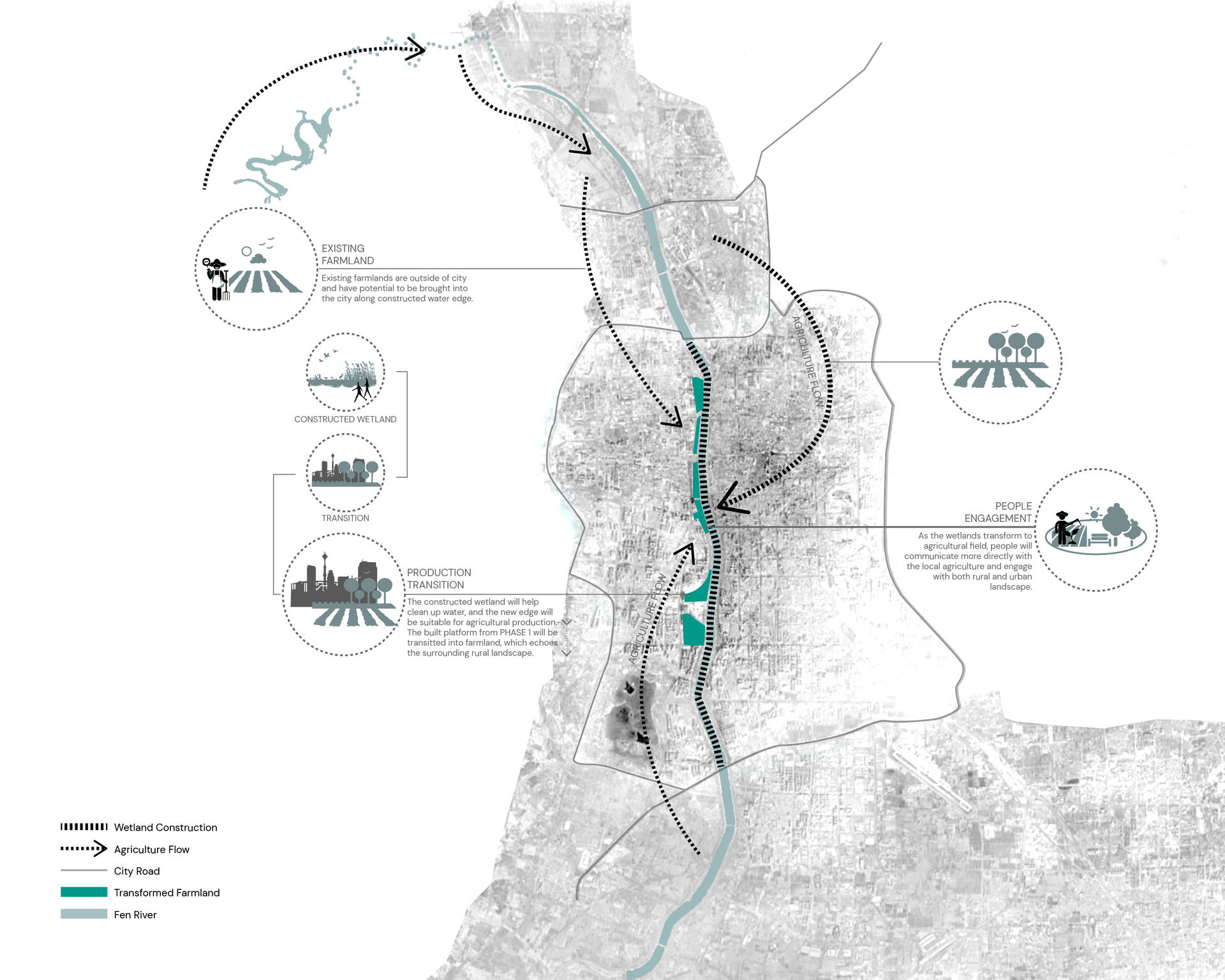
Phase 2 is transition and production. After water gets cleaned up, the water edge will be suitable for agricultural production. Then, the park space will be gradually transformed into farmland and bring the outer rural landscape into the city, which also echoes the rural landscape in the broader context. Besides the wetland areas, people can get involved with agricultural programs in the future.
Image
Image