Image

Jingjing Cui
Arctic Resilience: Adaptive Networks of Self-Sufficiency
In the new global study of machine-learning-based evidence and attribution mapping of 100,000 climate impact studies on Nature Climate Change, 80% of the world's land mass has been impacted by climate change, influencing most of the world's 7.7 billion people. Arctic amplification causes the region to experience climate change twice as fast as the rest of the planet due to sea ice loss and changes in atmospheric circulation. This results in severe impacts on Arctic coastal communities, including harsh weather, coastal erosion, and difficulties in winter hunting. Forced relocations to inner lands move communities away from their ancestral land, causing food insecurity and dependence on non-traditional food sources. Inefficient political and financial support exacerbates these challenges, leading to potential cultural, habitual, and psychological maladjustment. At present, many of these communities are experiencing a significant amount of resource wastage. Factors such as inefficient use of energy, water, and materials, combined with inadequate waste management systems, contribute to unsustainable living practices. This not only puts a strain on the already limited resources available in these Arctic coastal communities but also exacerbates their vulnerability to climate change impacts. The existing strategies are quite basic and meet the fundamental requirements, but they lack resilience in the face of drastic environmental changes and do not maximize resource utilization.
In this context, this thesis Arctic Resilience focuses on rearranging resources to design a closed-loop system to improve the Arctic coastal communities' self-sufficiency, resource utilization efficiency, and adaptability of the challenges faced during the relocation process and future settlement. By analyzing challenges, examining case studies, and identifying improvement opportunities, this thesis will develop a sustainable and adaptable model. To test the effectiveness of the proposed system, the final phase of the project thesis will evaluate its impact on various aspects and compare its performance to existing strategies.
Image

The Warming North
This image encapsulates the escalating repercussions of global warming, particularly the accelerated melting of Arctic sea ice. This ecological transformation is profoundly impacting the predominantly Indigenous villages that inhabit the Arctic region. As the polar amplification effect intensifies, these communities are facing increasingly profound environmental shifts and challenges.
Image
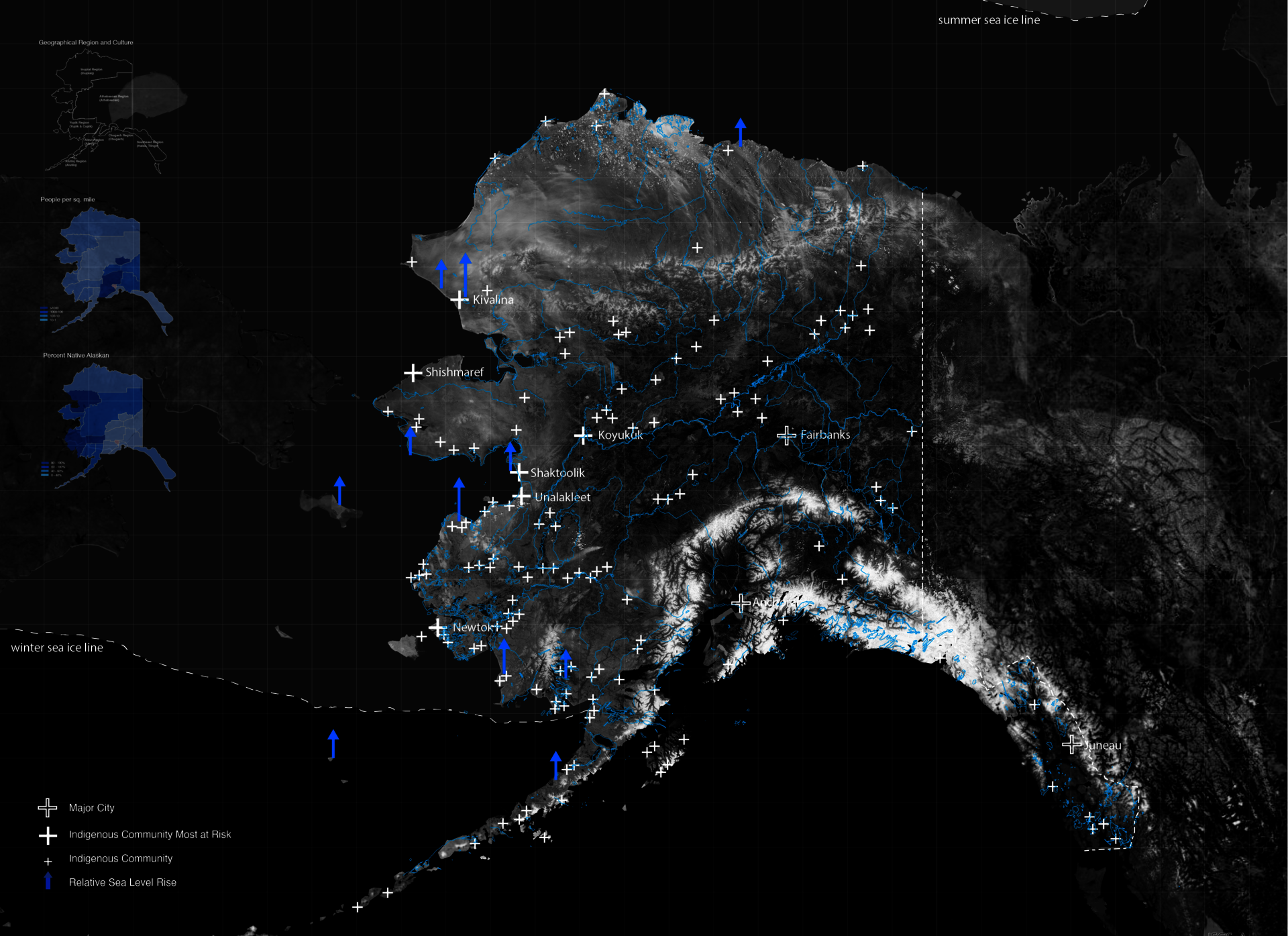
Alaska Villages & Sea-level Rise
The dire circumstances of five severely affected villages situated along the Alaskan coastline. These communities are confronted with the imminent threat of land loss, rendering them climate refugees. Dependent on the ocean for sustenance, they now find themselves compelled to adapt their subsistence practices due to the escalating impact of climate change. This situation necessitates urgent attention and the implementation of resilient strategies.
Image

Lifestyle Change
This delves into the intricate fabric of these communities' traditional survival practices, emphasizing the invaluable lessons that can be derived from their indigenous knowledge systems. Understanding their historical ways of life, cultural values, and sustainable resource management practices becomes paramount in developing effective and contextually appropriate adaptation strategies.
Image
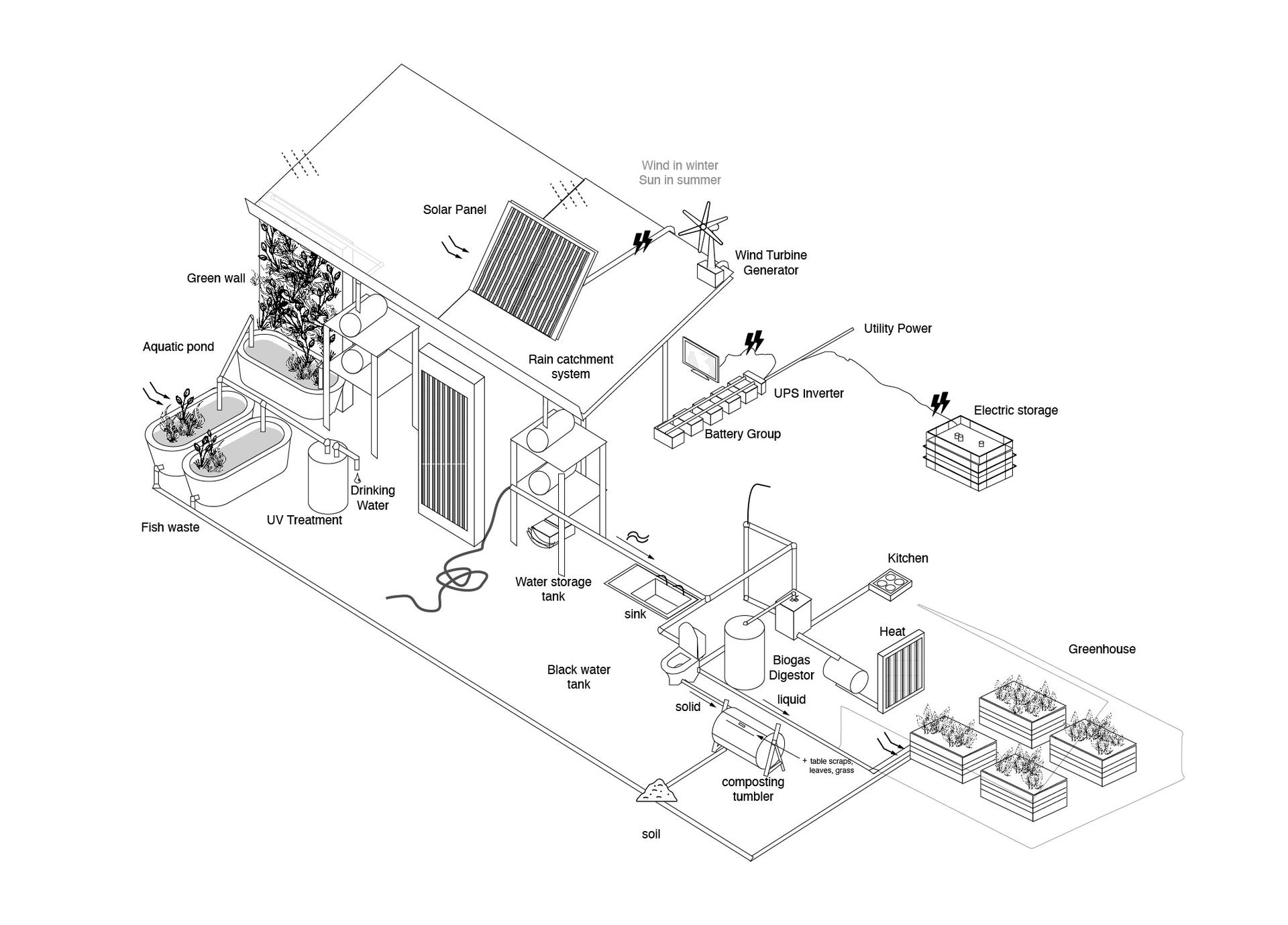
Closed-loop System
It's critical significance of optimizing resource utilization amidst the increasingly hostile environmental conditions. Implementing a closed-loop system, characterized by circular economies and minimal waste generation, provides a framework for enhancing resilience. By fostering adaptive behaviors that align with weather fluctuations, such as flexible resource allocation and dynamic energy management, these communities can enhance their capacity to withstand environmental stresses.
Image
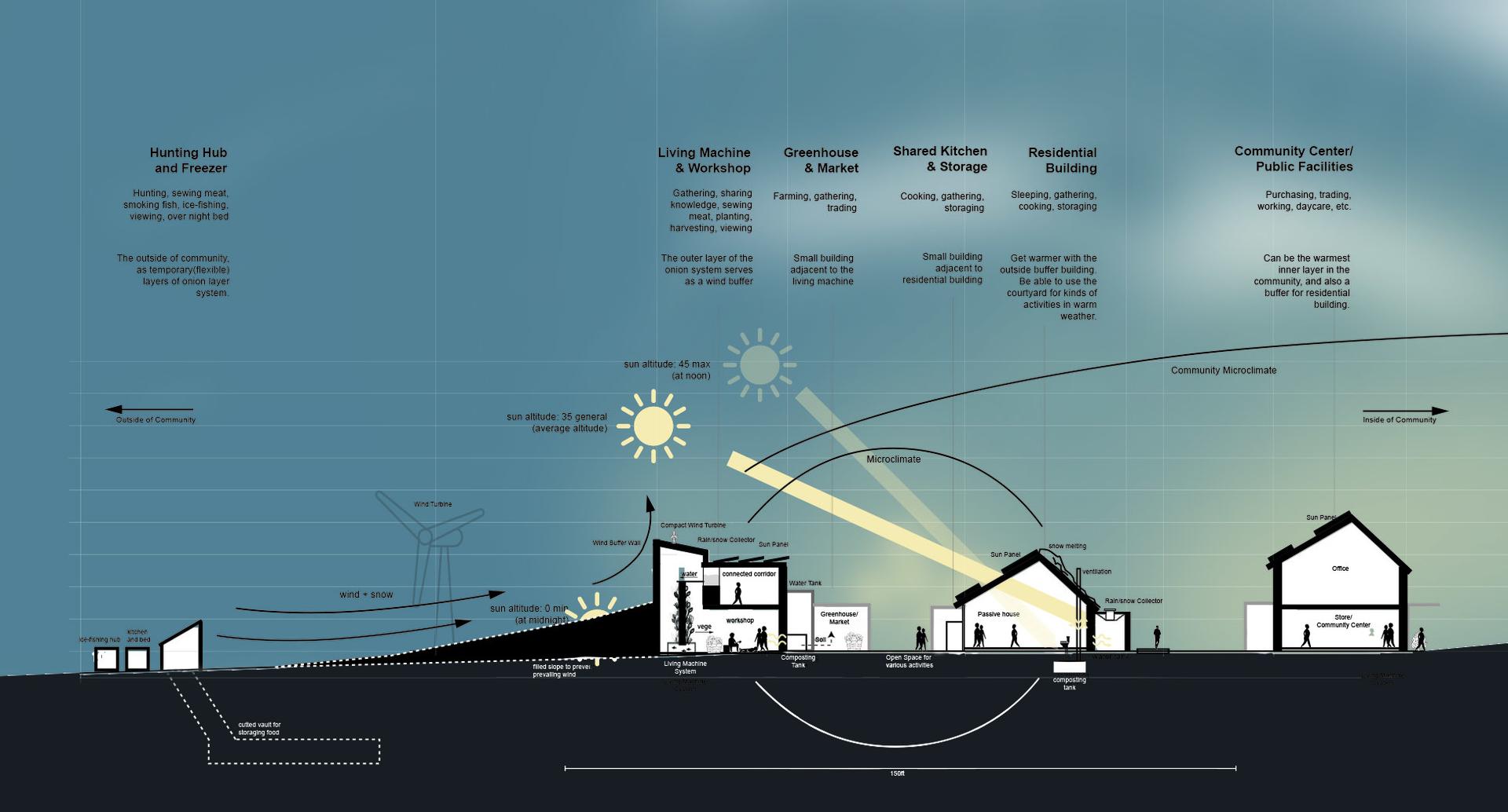
Onion Layers
The imperative of designing village layouts that effectively modulate microclimates to bolster disaster resilience. By strategically configuring the built environment to mitigate the impacts of severe weather phenomena, such as blizzards and prevailing winds, the village core adopts an onion-like structure. This spatial arrangement optimizes protection, facilitates efficient resource allocation, and fosters social cohesion, collectively enhancing the village's resilience.